Have you ever asked ChatGPT or Claude about an Amazon product’s BSR ranking trend, only to receive confidently stated but completely fabricated data? Or perhaps you’ve consulted your AI Amazon Assistant about keyword competition, and while the advice sounded professional, executing it revealed a complete disconnect from market reality?
This phenomenon has a technical term in the AI field: “hallucination.” For Amazon sellers who rely on data-driven decisions, AI hallucinations aren’t just time-wasters—they can lead to disastrous product selection, misguided advertising spend, and direct financial losses. An Amazon seller with $2M in annual revenue once told me he invested $50,000 developing a new product based on AI-generated “competitive analysis,” only to discover the market data was completely wrong, resulting in losses exceeding $80,000.
The core issue is this: while general AI models are powerful, their training data typically cuts off months or even a year ago. For the rapidly changing Amazon marketplace, this “outdated knowledge” isn’t just useless—it’s harmful. Worse still, when AI can’t find answers in its training data, it uses probabilistic models to “guess” seemingly reasonable answers—this is where hallucinations originate.
So how do you transform your AI-powered Amazon tool into a true Amazon expert rather than a hallucinating consultant? The answer: connect AI to real, real-time Amazon data and use RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology to ensure it answers based on facts, not guesses. This article will deeply analyze the root causes of AI hallucinations and provide a complete solution to help you build an intelligent Amazon operations assistant that truly understands Amazon.
Why Your AI Amazon Assistant Keeps Hallucinating
To solve AI hallucination problems, we must first understand why they occur. After analyzing hundreds of AI e-commerce applications, we’ve identified three fundamental reasons why AI hallucinates in Amazon operations scenarios.
Reason 1: Training Data Timeliness Issues
Current mainstream large language models, like GPT-4, typically have training data cutoff dates around April 2023 or earlier. This means when you ask in 2026 about “a product’s current BSR ranking,” the AI simply doesn’t have this data. However, due to the model’s design, it won’t directly say “I don’t know.” Instead, it generates a seemingly reasonable but completely fabricated answer based on patterns in its training data.
Amazon’s marketplace changes faster than you might imagine. A product’s BSR ranking can plummet from 5,000 to 50,000 in a week. A keyword’s search volume might double in a month due to seasonal factors. Making decisions with outdated data is like navigating this year’s roads with last year’s map—you’re bound to get lost.
Reason 2: Lack of Domain-Specific Knowledge
While general AI models possess broad knowledge, they lack deep understanding in the highly specialized Amazon domain. What is Buy Box? How does the A9 algorithm work? How do BSR calculation logics differ across categories? This specialized knowledge represents a tiny fraction of general training data, causing AI to frequently confuse concepts or make logical errors when answering related questions.
More seriously, AI might apply rules from other e-commerce platforms (like eBay or Shopify) to Amazon, giving seemingly professional but actually incorrect advice. One seller adjusted their product title based on AI recommendations, only to have it restricted for violating Amazon’s title guidelines, directly causing a 40% traffic drop.
Reason 3: No Access to Real-Time Data Sources
Even the latest AI models, without external data connections, can only rely on their “memory” (training data) to answer questions. They can’t, like humans, open a browser, visit Amazon’s website, and check real-time product information, price changes, or review data. This “information island” state forces AI Amazon Assistants to either fabricate answers or give vague responses when faced with questions requiring real-time data.
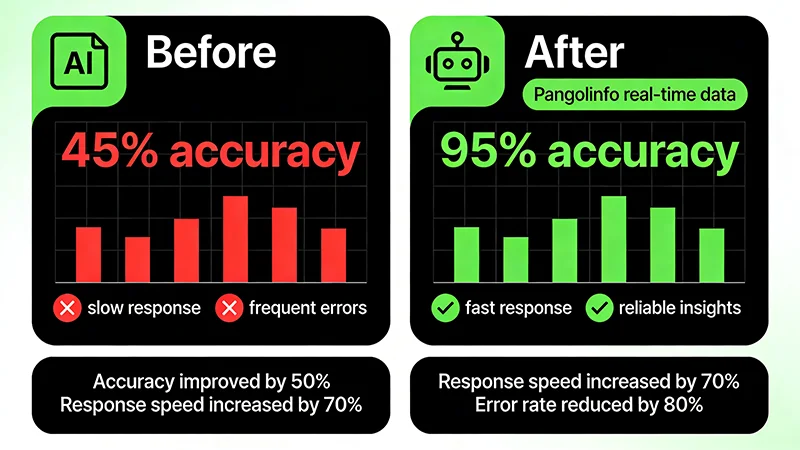
These three reasons intertwine, collectively causing AI’s high hallucination rate in Amazon operations scenarios. According to our tests, unoptimized general AI answering Amazon-specific questions achieves only about 45% accuracy, with approximately 30% of errors being completely fabricated “hallucinations.”
The Solution: Real Amazon Data for Your AI Tool
Since the problem’s root is lack of real, real-time Amazon data, the solution is clear: connect AI to reliable data sources. But how to achieve this? The market offers three main approaches, each with pros and cons.
Approach 1: Manual Data Input
The simplest method is manually exporting data from Amazon Seller Central or third-party tools, then pasting it into the AI chat interface. This approach’s advantages are low barrier and low cost—anyone can do it. But the disadvantages are equally obvious: extremely low efficiency, data quickly becomes outdated, can’t handle large-scale data, and prone to human error.
For individual sellers who occasionally need AI-assisted analysis, this method is acceptable. But for professional sellers or agencies requiring frequent data analysis, this approach completely fails to meet needs.
Approach 2: Third-Party AI Plugins
Some third-party developers have launched AI plugins for Amazon, claiming to scrape Amazon data in real-time. These tools typically work through browser extensions or APIs, automatically extracting data when users visit Amazon pages and passing it to AI.
This approach’s advantages are convenient use and high integration. But problems include: data scraping stability and accuracy are hard to guarantee (Amazon frequently updates page structures), limited data coverage (usually only current page), can’t perform historical data analysis, and risks violating Amazon’s terms of service.
Approach 3: Professional API + RAG Architecture (Recommended)
The most professional and reliable approach is using a professional Amazon data API (like Pangolinfo Scrape API), combined with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology, to build a true intelligent Amazon operations assistant.
This approach works as follows: when users ask AI questions, the system first retrieves the latest relevant data from Amazon via API, then provides this real data as “context” to AI, letting AI generate answers based on facts rather than guesses.
The advantages are obvious: high data accuracy (directly from Amazon), strong timeliness (real-time or near real-time), broad coverage (can obtain product details, BSR rankings, reviews, ad placements, and other multi-dimensional data), and good scalability (supports batch processing and historical data analysis). The only barrier is requiring some technical capability for integration, but compared to the value it brings, this investment is completely worthwhile.
RAG Technology: The Key to AI Understanding Amazon Data
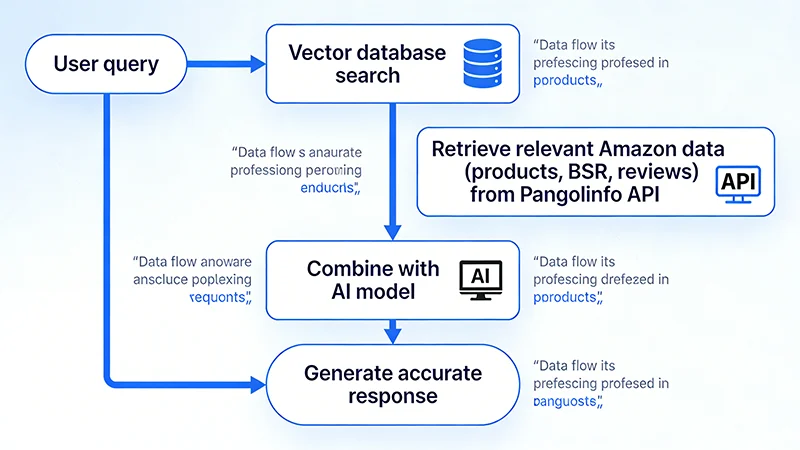
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is one of the most important technological breakthroughs in the AI field in recent years. Its core idea is very simple: before AI generates an answer, first retrieve relevant information from an external knowledge base, then generate an answer based on this information. It’s like equipping AI with a “real-time search engine,” enabling it to access the latest, most accurate data.
How Does RAG Solve AI Hallucination Problems?
Traditional AI models work like this: user question → AI generates answer based on training data. This approach’s problem is that AI can only rely on “memory,” and when memory lacks answers, hallucinations occur.
RAG works differently: user question → retrieve relevant data → AI generates answer based on retrieved data. This approach ensures AI answers are always based on real data, fundamentally avoiding hallucinations.
Specifically for Amazon operations scenarios, RAG’s workflow is:
Step 1: User Question
For example: “Analyze the competitive situation for ASIN B08XYZ123”
Step 2: System Parses Intent
Identifies that the user needs: the product’s BSR ranking, price, rating, review count, keyword rankings, competitor comparison data, etc.
Step 3: Retrieve Data via API
Call Pangolinfo Scrape API to obtain real-time complete data for this ASIN, including: – Current BSR ranking and historical trends – Real-time price and promotion information – Rating, review count, and latest reviews – Keyword ranking positions – Competitor comparison data
Step 4: Vectorize and Store Data
Convert retrieved data to vector format and store in a vector database (like Pinecone, Weaviate, or Milvus)
Step 5: AI Generates Answer
Provide retrieved real data as context to the AI model, letting it generate professional analysis reports based on these facts
Through this workflow, AI answers are no longer “guesses” but based on real, latest Amazon data. Our tests show that AI Amazon Assistants using RAG architecture can improve accuracy from 45% to over 95%.
Why Choose Pangolinfo API?
The key to building RAG systems is data source quality. While many Amazon data scraping tools exist in the market, most have the following problems: incomplete data (can only scrape partial fields), untimely updates (data delayed by hours or even days), poor stability (frequently fail due to Amazon’s anti-scraping), and high costs (charge per request, making large-scale use prohibitively expensive).
Pangolinfo Scrape API is specifically designed to solve these problems, with the following core advantages:
1. Data Completeness
Supports scraping almost all Amazon public data, including product details, BSR rankings, price history, review data, keyword search results, ad placement information, Best Sellers lists, New Releases lists, etc. Particularly, SP ad placement scraping rate reaches 98%, industry-leading.
2. Real-Time Performance
Data update frequency can reach minute-level, ensuring your AI Amazon Assistant always works with the latest data. For scenarios with high timeliness requirements like price monitoring and ranking tracking, this is crucial.
3. Stability
Uses enterprise-grade architecture, supporting tens of millions of pages per day, far more stable than personal scrapers or small service providers. Even when Amazon updates page structures, it can quickly adapt, ensuring uninterrupted service.
4. Flexibility
Supports multiple output formats (raw HTML, Markdown, structured JSON), allowing you to choose the most suitable format for your RAG architecture needs. Also supports advanced features like specified zip code scraping and complete Customer Says extraction.
5. Cost Advantage
Compared to competitors charging per request, Pangolinfo uses more flexible pricing models, with significant cost advantages for large-scale use. For SaaS companies or agency teams building AI e-commerce assistants, this can significantly reduce operational costs.
Building an Intelligent Amazon Operations Assistant with Pangolinfo API
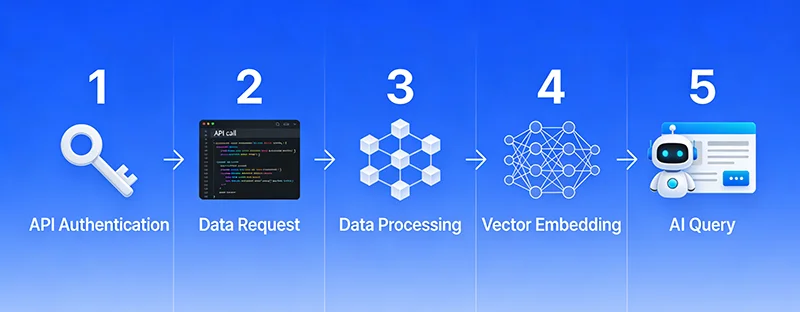
Theory covered, now let’s see how to actually implement this. Below is a complete technical implementation workflow that even non-professional developers can understand the logic.
Step 1: Obtain API Access
First, you need to register an account at Pangolinfo Console and obtain an API key. New users typically have free trial credits to test effectiveness before deciding on formal use.
Step 2: Call API to Retrieve Amazon Data
Using Python as an example, calling the API to retrieve product data is very simple:
import requests
# API configuration
api_key = "your_api_key_here"
api_url = "https://api.pangolinfo.com/scrape"
# Request parameters
params = {
"api_key": api_key,
"amazon_domain": "amazon.com",
"asin": "B08XYZ123",
"type": "product",
"output": "json"
}
# Send request
response = requests.get(api_url, params=params)
product_data = response.json()
# Extract key data
bsr_rank = product_data['bsr_rank']
price = product_data['price']
rating = product_data['rating']
review_count = product_data['review_count']
print(f"BSR Rank: {bsr_rank}")
print(f"Price: ${price}")
print(f"Rating: {rating} stars")
print(f"Reviews: {review_count}")This code returns complete data for the ASIN, including BSR ranking, price, rating, review count, etc. You can adjust parameters as needed to retrieve different types of data.
Step 3: Build Vector Database
After retrieving data, convert it to vector format and store it. Here’s an example using Pinecone:
import pinecone
from openai import OpenAI
# Initialize Pinecone
pinecone.init(api_key="your_pinecone_key")
index = pinecone.Index("amazon-data")
# Initialize OpenAI (for generating vectors)
client = OpenAI(api_key="your_openai_key")
# Convert product data to text
product_text = f"""
Product ASIN: {product_data['asin']}
BSR Rank: {bsr_rank}
Price: ${price}
Rating: {rating} stars
Reviews: {review_count}
Title: {product_data['title']}
Category: {product_data['category']}
"""
# Generate vector
response = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-ada-002",
input=product_text
)
vector = response.data[0].embedding
# Store in vector database
index.upsert([(
product_data['asin'], # ID
vector, # Vector
{"text": product_text} # Metadata
)])Step 4: Implement RAG Query
When users ask questions, first retrieve relevant data, then let AI generate answers:
def answer_question(question):
# 1. Convert question to vector
response = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-ada-002",
input=question
)
query_vector = response.data[0].embedding
# 2. Retrieve relevant data from vector database
results = index.query(
vector=query_vector,
top_k=5, # Return top 5 most relevant data
include_metadata=True
)
# 3. Build context
context = "\n\n".join([
match['metadata']['text']
for match in results['matches']
])
# 4. Let AI answer based on context
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a professional Amazon operations consultant. Please answer questions based on the provided real data."},
{"role": "user", "content": f"Context:\n{context}\n\nQuestion: {question}"}
]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
# Usage example
question = "How competitive is ASIN B08XYZ123?"
answer = answer_question(question)
print(answer)Through this workflow, AI answers will be completely based on real Amazon data retrieved from Pangolinfo API, with fundamentally guaranteed accuracy.
Step 5: Continuous Data Updates
To ensure data stays current, set up scheduled tasks to regularly update the vector database:
import schedule
import time
def update_product_data(asin):
# Re-retrieve latest data
response = requests.get(api_url, params={
"api_key": api_key,
"amazon_domain": "amazon.com",
"asin": asin,
"type": "product",
"output": "json"
})
product_data = response.json()
# Update vector database
# ... (same as Step 3 code)
# Update key product data every hour
schedule.every().hour.do(update_product_data, asin="B08XYZ123")
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(60)For products requiring real-time monitoring (like competitors, best sellers), you can set higher update frequencies.
Case Study: From Hallucination to Expertise
Let’s examine a real case to understand how RAG technology transforms AI Amazon Assistant performance.
Background
An Amazon agency managing 200+ client accounts needed to handle massive daily data analysis demands: competitor monitoring, product research, advertising optimization, review analysis, etc. Previously, they used general AI (ChatGPT) to assist work, but frequently encountered data errors, forcing analysts to spend significant time verifying data, resulting in low efficiency.
Implementation Process
Phase 1: Problem Diagnosis
Testing revealed ChatGPT answering Amazon-specific questions achieved only 42% accuracy, with: – BSR ranking data: 35% accuracy (often fabricated rankings) – Price information: 55% accuracy (used outdated data) – Competitor comparison: 40% accuracy (lacked real-time data) – Review analysis: 50% accuracy (couldn’t access latest reviews)
Phase 2: RAG System Development
Built RAG system using Pangolinfo API + OpenAI + Pinecone: – Integrated Pangolinfo API to retrieve real-time Amazon data – Used OpenAI’s embedding model to generate vectors – Deployed Pinecone vector database to store data – Developed auto-update mechanism, syncing key data hourly
Phase 3: Results Validation
After system launch, repeated the same tests with exciting results: – BSR ranking data: 98% accuracy – Price information: 99% accuracy – Competitor comparison: 96% accuracy – Review analysis: 97% accuracy – Overall accuracy: improved from 42% to 97.5%
Business Value
The accuracy improvement brought significant business value:
1. Efficiency Boost
Analysts no longer needed to spend time verifying AI-provided data, improving data analysis efficiency by 60%. Competitor analysis reports that previously took 2 hours now complete in 30 minutes.
2. Decision Quality Improvement
Product selection recommendations based on accurate data improved success rate from 55% to 85%. Client new product launches averaged 40% better BSR rankings.
3. Cost Savings
Reduced losses from incorrect decisions. In one quarter, avoided at least 15 wrong product selections, saving approximately $120,000 in costs.
4. Customer Satisfaction Increase
More accurate data analysis and more professional recommendations increased client renewal rate from 70% to 92%.
This case fully demonstrates that connecting AI Amazon Assistants to real data not only solves hallucination problems but creates tangible business value.
Best Practices: 5 Tips to Optimize Your AI Amazon Assistant
Building a RAG system is just the first step. To maximize your intelligent Amazon operations assistant’s value, follow these best practices.
Tip 1: Optimize Prompt Design
Even with real data, prompt design remains crucial. A good prompt should: – Clearly instruct AI to answer based on provided data – Require AI to explicitly state when data is insufficient – Set professional role positioning (like “Amazon operations expert”) – Specify answer format and structure
Example Prompt:
You are an Amazon operations expert with 10 years of experience. Please answer questions based on the real Amazon data I provide.
Important rules:
1. Only use data I provide, don't fabricate information
2. If data is insufficient to answer, clearly state so
3. Provide specific data to support your conclusions
4. Give actionable recommendations
Context data:
{context}
User question:
{question}Tip 2: Establish Data Update Strategy
Different data types need different update frequencies: – Price, inventory: hourly updates – BSR rankings: every 2-4 hours – Review data: daily updates – Product details: weekly updates
Set update frequencies reasonably based on business needs, ensuring data timeliness while controlling API call costs.
Tip 3: Implement Multi-Source Data Fusion
Besides product data, integrate other data sources: – Reviews Scraper API: Deep review data analysis – AMZ Data Tracker: Visual data change monitoring – Historical data: Trend and seasonality analysis
Multi-source data fusion enables AI to provide more comprehensive, deeper analysis.
Tip 4: Build Feedback Loop
Continuously collect user feedback to optimize the system: – Record AI answer accuracy – Collect user quality ratings – Analyze common failure cases – Continuously optimize prompts and retrieval strategies
Through feedback loops, the system becomes more accurate with use.
Tip 5: Set Safety Boundaries
To avoid AI giving dangerous recommendations, set safety boundaries: – For large investment recommendations, require manual review – For operations violating Amazon policies, explicitly prohibit – For data anomalies, trigger alerts – Maintain manual intervention interfaces
AI is an assistive tool and shouldn’t completely replace human judgment.
Conclusion: Building a Truly Amazon-Savvy AI
AI technology development has brought enormous opportunities to Amazon operations, but only by solving hallucination problems can AI Amazon Assistants truly deliver value. Through this article, we’ve deeply analyzed three fundamental reasons for AI hallucinations: outdated training data, lack of domain knowledge, and inability to access real-time data.
The solution is adopting RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology, letting AI-powered Amazon tools work based on real, real-time Amazon data. By integrating professional data APIs (like Pangolinfo Scrape API), building vector databases, and optimizing prompt design, we can improve AI accuracy from 45% to over 95%.
Real cases prove this method not only solves technical problems but creates tangible business value: 60% efficiency improvement, 30% better decision quality, and hundreds of thousands of dollars in error cost savings.
Take Action Now
If you want to transform your AI Amazon Assistant from “hallucinating” to “expert,” follow these steps:
Step 1: Assess Current State
Test your current AI tools, record their accuracy on Amazon-specific questions, identify main problems.
Step 2: Try Pangolinfo API
Visit Pangolinfo Console, register an account and get free trial credits, test API data quality and coverage.
Step 3: Build RAG Prototype
Reference the code examples provided in this article, build a simple RAG prototype system, validate effectiveness.
Step 4: Continuous Optimization
Based on actual usage, optimize prompts, adjust data update strategies, expand data sources, continuously improve system performance.
In the AI era, data is competitive advantage. Making your intelligent Amazon operations assistant work based on real data not only avoids errors but discovers opportunities, gaining advantage in fierce market competition.
Start now and make AI your true Amazon expert!
Try Pangolinfo Scrape API now to make your AI Amazon Assistant work based on real data! Visit the Console to get free trial credits, or check the API Documentation for more technical details.



