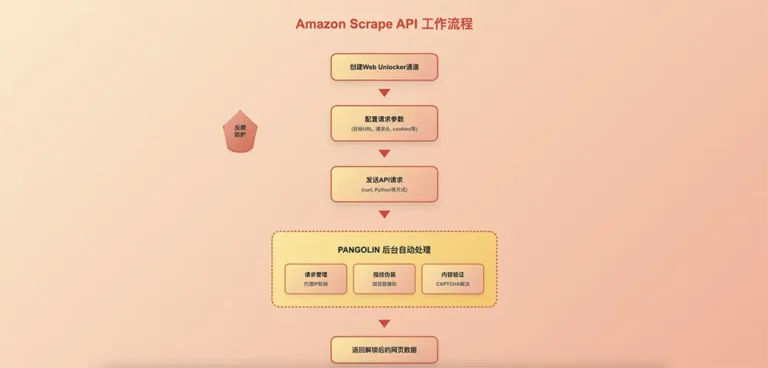
在当今竞争激烈的电商环境中,获取准确、及时的市场数据已成为企业制胜的关键。无论你是电商卖家、数据分析师还是开发者,掌握高效的数据抓取技术都至关重要。本文将为你详细介绍如何使用Pangolin API接口调用来实现Amazon数据的自动化采集,让你轻松获取竞争对手信息、市场趋势和产品数据。
什么是Pangolin Scrape API?
Pangolin是一个专业的Amazon数据抓取服务平台,提供稳定可靠的Scrape API接口,帮助用户高效获取电商平台的各类数据。通过Pangolin的Amazon数据抓取API教程,你可以轻松实现:
- 产品信息批量采集
- 价格监控和分析
- 竞争对手数据跟踪
- 市场趋势研究
- 客户评价分析
与传统的网页爬虫相比,Pangolin API具有更高的稳定性和成功率,同时避免了反爬虫机制的困扰。
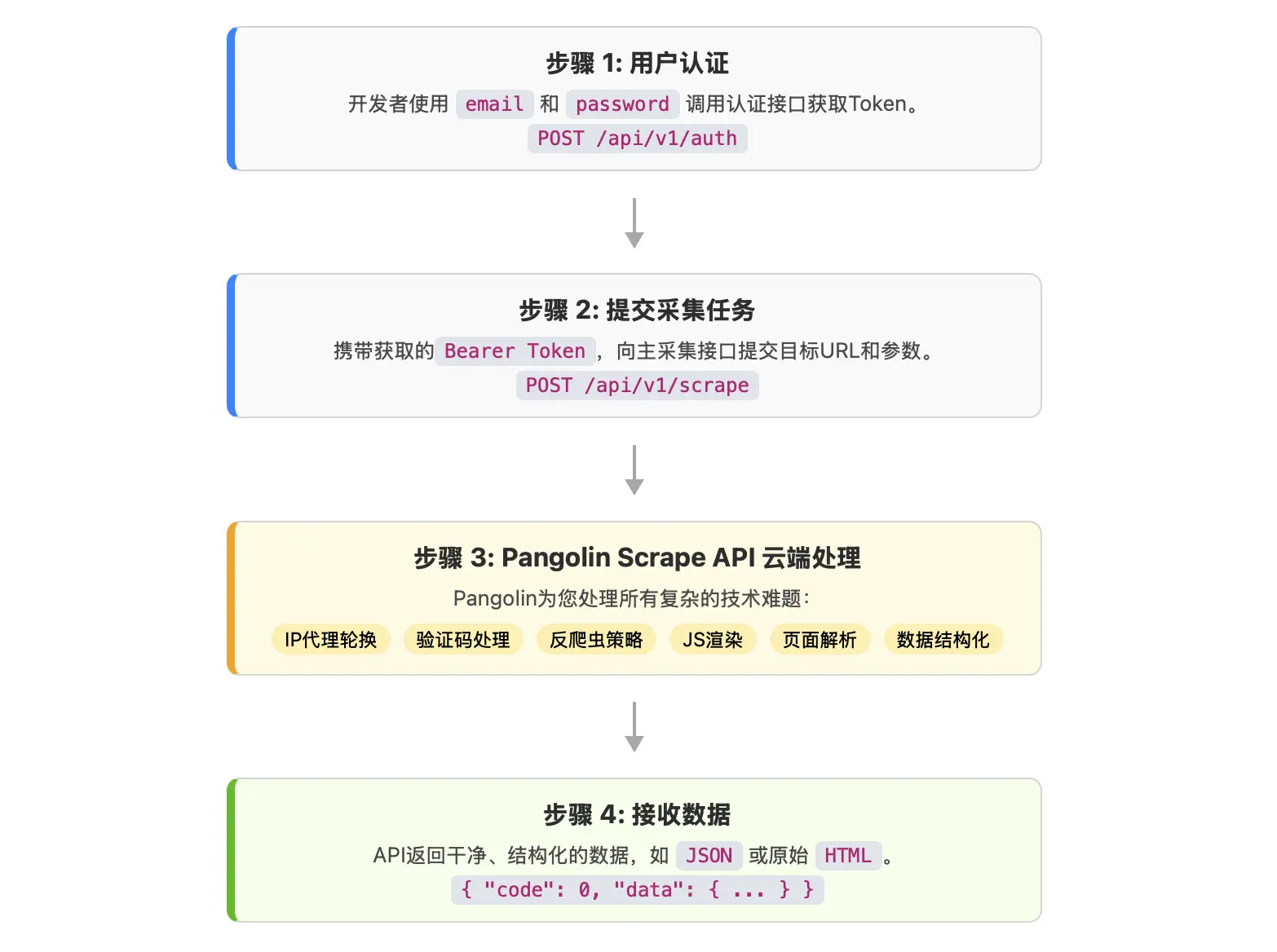
准备工作:开始之前你需要了解的
1. 注册Pangolin账户
首先,你需要访问Pangolin官网完成账户注册。注册过程简单快捷,只需提供基本信息即可。注册成功后,你将获得:
- 专属的API密钥(API Key)
- 接口调用权限
- 技术文档访问权限
- 客服支持服务
2. 获取API凭证
登录你的Pangolin账户后台,在”API管理”页面可以找到你的API凭证信息。这些凭证包括:
API Key: your_api_key_here
Secret Key: your_secret_key_here
Base URL: https://api.pangolinfo.com
请妥善保管这些信息,避免泄露给第三方。
3. 开发环境配置
根据你的开发需求,确保开发环境中已安装相应的HTTP请求库:
Python环境:
pip install requests
pip install json
pip install pandas # 用于数据处理
Node.js环境:
npm install axios
npm install fs-extra
Pangolin爬虫接口使用方法详解
核心接口概览
Pangolin提供了多个核心接口,每个接口都有特定的功能:
- 产品搜索接口 – 根据关键词搜索产品
- 产品详情接口 – 获取单个产品的详细信息
- 价格历史接口 – 查询产品的价格变化历史
- 评价数据接口 – 抓取产品评价和评分
- 卖家信息接口 – 获取卖家的详细资料
基础调用示例
下面是一个基础的Pangolin API接口调用示例,展示如何获取产品信息:
import requests
import json
# 配置API信息
API_KEY = "your_api_key_here"
BASE_URL = "https://api.pangolinfo.com"
# 设置请求头
headers = {
'Authorization': f'Bearer {API_KEY}',
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'User-Agent': 'Pangolin-Client/1.0'
}
# 产品搜索请求
def search_products(keyword, marketplace='US'):
url = f"{BASE_URL}/v1/search"
payload = {
'keyword': keyword,
'marketplace': marketplace,
'page': 1,
'per_page': 20
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求失败: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
keyword = "wireless earbuds"
result = search_products(keyword)
if result:
print(f"找到 {len(result['products'])} 个产品")
for product in result['products']:
print(f"产品名称: {product['title']}")
print(f"价格: {product['price']}")
print(f"ASIN: {product['asin']}")
print("-" * 50)
高级功能实现
1. 批量数据采集
对于需要采集大量数据的场景,建议使用批量处理方式:
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def batch_collect_products(asin_list):
"""批量采集产品信息"""
def get_product_detail(asin):
url = f"{BASE_URL}/v1/product/{asin}"
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception as e:
print(f"采集ASIN {asin} 失败: {e}")
return None
# 使用线程池并发处理
results = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(get_product_detail, asin) for asin in asin_list]
for future in futures:
result = future.result()
if result:
results.append(result)
time.sleep(0.5) # 控制请求频率
return results
# 使用示例
asin_list = ['B08C1W5N87', 'B09JQM7P4X', 'B08HLYJHTN']
products = batch_collect_products(asin_list)
2. 价格监控功能
实现自动化的价格监控是电商数据采集API集成的重要应用:
import schedule
import time
from datetime import datetime
class PriceMonitor:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.api_key = api_key
self.monitored_products = []
def add_product(self, asin, target_price=None):
"""添加监控产品"""
self.monitored_products.append({
'asin': asin,
'target_price': target_price,
'last_price': None,
'price_history': []
})
def check_prices(self):
"""检查价格变化"""
for product in self.monitored_products:
url = f"{BASE_URL}/v1/product/{product['asin']}/price"
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
current_data = response.json()
current_price = float(current_data['current_price'])
# 记录价格历史
product['price_history'].append({
'price': current_price,
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
# 价格变化提醒
if product['last_price'] and current_price != product['last_price']:
change = current_price - product['last_price']
print(f"产品 {product['asin']} 价格变化: {change:+.2f}")
# 目标价格提醒
if product['target_price'] and current_price <= product['target_price']:
print(f"? 产品 {product['asin']} 已达到目标价格!")
product['last_price'] = current_price
except Exception as e:
print(f"价格检查失败: {e}")
# 使用价格监控
monitor = PriceMonitor(API_KEY)
monitor.add_product('B08C1W5N87', target_price=29.99)
# 定时执行价格检查
schedule.every(1).hour.do(monitor.check_prices)
# 运行监控
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(60)
Pangolin Scrape API开发指南进阶技巧
1. 错误处理和重试机制
在实际应用中,网络请求可能会遇到各种问题。建议实现完善的错误处理机制:
import time
from functools import wraps
def retry_on_failure(max_retries=3, delay=1, backoff=2):
"""重试装饰器"""
def decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
retries = 0
while retries < max_retries:
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
retries += 1
if retries == max_retries:
raise e
time.sleep(delay * (backoff ** (retries - 1)))
return None
return wrapper
return decorator
@retry_on_failure(max_retries=3)
def robust_api_call(url, payload=None):
"""带重试机制的API调用"""
if payload:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
else:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
2. 数据清洗和格式化
获取原始数据后,通常需要进行清洗和格式化:
import re
from decimal import Decimal
class DataCleaner:
@staticmethod
def clean_price(price_str):
"""清洗价格数据"""
if not price_str:
return None
# 提取数字部分
price_match = re.search(r'[\d,]+\.?\d*', str(price_str))
if price_match:
clean_price = price_match.group().replace(',', '')
return float(clean_price)
return None
@staticmethod
def clean_title(title):
"""清洗产品标题"""
if not title:
return ""
# 移除多余空格和特殊字符
clean_title = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', title.strip())
clean_title = re.sub(r'[^\w\s\-\(\)]', '', clean_title)
return clean_title
@staticmethod
def extract_rating(rating_str):
"""提取评分数值"""
if not rating_str:
return None
rating_match = re.search(r'(\d+\.?\d*)', str(rating_str))
if rating_match:
return float(rating_match.group())
return None
# 使用数据清洗
cleaner = DataCleaner()
raw_data = {
'title': ' Wireless Earbuds - Premium Quality!!! ',
'price': '$39.99',
'rating': '4.5 out of 5 stars'
}
cleaned_data = {
'title': cleaner.clean_title(raw_data['title']),
'price': cleaner.clean_price(raw_data['price']),
'rating': cleaner.extract_rating(raw_data['rating'])
}
3. 数据存储和管理
对于采集到的数据,建议使用合适的存储方案:
import sqlite3
import pandas as pd
from datetime import datetime
class DataManager:
def __init__(self, db_path="pangolin_data.db"):
self.db_path = db_path
self.init_database()
def init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
asin TEXT UNIQUE,
title TEXT,
price REAL,
rating REAL,
reviews_count INTEGER,
category TEXT,
brand TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
''')
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS price_history (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
asin TEXT,
price REAL,
timestamp TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (asin) REFERENCES products (asin)
)
''')
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def save_product(self, product_data):
"""保存产品数据"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
INSERT OR REPLACE INTO products
(asin, title, price, rating, reviews_count, category, brand, updated_at)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', (
product_data.get('asin'),
product_data.get('title'),
product_data.get('price'),
product_data.get('rating'),
product_data.get('reviews_count'),
product_data.get('category'),
product_data.get('brand'),
datetime.now()
))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def get_products_by_category(self, category):
"""按类别获取产品"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
df = pd.read_sql_query(
"SELECT * FROM products WHERE category = ?",
conn, params=(category,)
)
conn.close()
return df
# 使用数据管理器
data_manager = DataManager()
性能优化建议
1. 请求频率控制
为了避免触发反爬虫机制,建议合理控制请求频率:
import time
from threading import Lock
class RateLimiter:
def __init__(self, max_requests=60, time_window=60):
self.max_requests = max_requests
self.time_window = time_window
self.requests = []
self.lock = Lock()
def wait_if_needed(self):
with self.lock:
now = time.time()
# 清理过期请求记录
self.requests = [req_time for req_time in self.requests
if now - req_time < self.time_window]
if len(self.requests) >= self.max_requests:
sleep_time = self.time_window - (now - self.requests[0])
if sleep_time > 0:
time.sleep(sleep_time)
self.requests = []
self.requests.append(now)
# 使用频率限制器
rate_limiter = RateLimiter(max_requests=30, time_window=60)
def controlled_api_call(url, payload=None):
rate_limiter.wait_if_needed()
return robust_api_call(url, payload)
2. 缓存机制
实现合理的缓存可以显著提高效率:
import hashlib
import json
import os
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class APICache:
def __init__(self, cache_dir="api_cache", default_ttl=3600):
self.cache_dir = cache_dir
self.default_ttl = default_ttl
os.makedirs(cache_dir, exist_ok=True)
def _get_cache_key(self, url, params=None):
"""生成缓存键"""
cache_str = url + str(params or {})
return hashlib.md5(cache_str.encode()).hexdigest()
def get(self, key):
"""获取缓存"""
cache_file = os.path.join(self.cache_dir, f"{key}.json")
if not os.path.exists(cache_file):
return None
try:
with open(cache_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
cache_data = json.load(f)
expire_time = datetime.fromisoformat(cache_data['expire_time'])
if datetime.now() > expire_time:
os.remove(cache_file)
return None
return cache_data['data']
except:
return None
def set(self, key, data, ttl=None):
"""设置缓存"""
ttl = ttl or self.default_ttl
expire_time = datetime.now() + timedelta(seconds=ttl)
cache_data = {
'data': data,
'expire_time': expire_time.isoformat()
}
cache_file = os.path.join(self.cache_dir, f"{key}.json")
with open(cache_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(cache_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
# 带缓存的API调用
cache = APICache()
def cached_api_call(url, payload=None, cache_ttl=3600):
cache_key = cache._get_cache_key(url, payload)
# 尝试从缓存获取
cached_result = cache.get(cache_key)
if cached_result:
return cached_result
# 调用API
result = controlled_api_call(url, payload)
if result:
cache.set(cache_key, result, cache_ttl)
return result
实战应用场景
1. 竞争对手价格监控
class CompetitorMonitor:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.api = PangolinAPI(api_key)
self.competitors = {}
def add_competitor_product(self, competitor_name, asin, our_asin=None):
"""添加竞争对手产品"""
if competitor_name not in self.competitors:
self.competitors[competitor_name] = []
self.competitors[competitor_name].append({
'asin': asin,
'our_asin': our_asin,
'price_alerts': []
})
def analyze_pricing_strategy(self, competitor_name):
"""分析竞争对手定价策略"""
products = self.competitors.get(competitor_name, [])
analysis = {
'avg_price': 0,
'price_range': (0, 0),
'pricing_trend': 'stable'
}
prices = []
for product in products:
product_data = self.api.get_product_detail(product['asin'])
if product_data and product_data.get('price'):
prices.append(float(product_data['price']))
if prices:
analysis['avg_price'] = sum(prices) / len(prices)
analysis['price_range'] = (min(prices), max(prices))
return analysis
# 使用竞争对手监控
monitor = CompetitorMonitor(API_KEY)
monitor.add_competitor_product("Brand A", "B08C1W5N87", our_asin="B08D123456")
pricing_analysis = monitor.analyze_pricing_strategy("Brand A")
2. 市场趋势分析
def analyze_category_trends(category_keywords, time_period_days=30):
"""分析品类趋势"""
trend_data = {
'keywords': category_keywords,
'period': time_period_days,
'trends': []
}
for keyword in category_keywords:
# 搜索相关产品
search_results = search_products(keyword)
if search_results and 'products' in search_results:
products = search_results['products']
# 计算平均价格、评分等指标
prices = [p.get('price', 0) for p in products if p.get('price')]
ratings = [p.get('rating', 0) for p in products if p.get('rating')]
trend_info = {
'keyword': keyword,
'total_products': len(products),
'avg_price': sum(prices) / len(prices) if prices else 0,
'avg_rating': sum(ratings) / len(ratings) if ratings else 0,
'top_brands': extract_top_brands(products)
}
trend_data['trends'].append(trend_info)
return trend_data
def extract_top_brands(products):
"""提取热门品牌"""
brand_count = {}
for product in products:
brand = product.get('brand', 'Unknown')
brand_count[brand] = brand_count.get(brand, 0) + 1
# 按出现次数排序
sorted_brands = sorted(brand_count.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return sorted_brands[:5]
# 分析无线耳机市场趋势
keywords = ['wireless earbuds', 'bluetooth headphones', 'noise cancelling earphones']
trend_analysis = analyze_category_trends(keywords)
常见问题解决方案
1. API调用失败处理
当遇到API调用失败时,可以按照以下步骤排查:
def diagnose_api_issue(url, payload=None):
"""诊断API问题"""
diagnostics = {
'url_valid': False,
'auth_valid': False,
'payload_valid': False,
'rate_limit_ok': False,
'server_response': None
}
# 检查URL格式
try:
from urllib.parse import urlparse
parsed = urlparse(url)
diagnostics['url_valid'] = bool(parsed.scheme and parsed.netloc)
except:
pass
# 检查认证信息
if 'Authorization' in headers:
diagnostics['auth_valid'] = True
# 检查payload格式
if payload is None or isinstance(payload, dict):
diagnostics['payload_valid'] = True
# 尝试发送请求
try:
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=30)
diagnostics['server_response'] = {
'status_code': response.status_code,
'headers': dict(response.headers),
'content': response.text[:500] # 前500字符
}
if response.status_code != 429: # 非频率限制错误
diagnostics['rate_limit_ok'] = True
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
diagnostics['server_response'] = str(e)
return diagnostics
# 使用诊断工具
if not result:
diagnosis = diagnose_api_issue(url, payload)
print("API调用诊断结果:", json.dumps(diagnosis, indent=2))
2. 数据质量验证
确保采集到的数据质量:
def validate_product_data(product):
"""验证产品数据质量"""
validation_result = {
'is_valid': True,
'errors': [],
'warnings': []
}
# 必需字段检查
required_fields = ['asin', 'title', 'price']
for field in required_fields:
if not product.get(field):
validation_result['errors'].append(f"缺少必需字段: {field}")
validation_result['is_valid'] = False
# 数据格式检查
if product.get('price'):
try:
price = float(product['price'])
if price <= 0:
validation_result['warnings'].append("价格值异常")
except ValueError:
validation_result['errors'].append("价格格式无效")
validation_result['is_valid'] = False
if product.get('rating'):
try:
rating = float(product['rating'])
if not (0 <= rating <= 5):
validation_result['warnings'].append("评分超出正常范围")
except ValueError:
validation_result['warnings'].append("评分格式无效")
# ASIN格式检查
if product.get('asin'):
asin = product['asin']
if not re.match(r'^[A-Z0-9]{10}$', asin):
validation_result['warnings'].append("ASIN格式可能有误")
return validation_result
总结与展望
通过本篇Pangolin API接口调用教程,我们详细介绍了从基础配置到高级应用的完整流程。掌握这些技能后,你可以:
- 高效采集Amazon数据 – 利用稳定的API接口获取准确的产品信息
- 构建自动化监控系统 – 实现价格、库存、评价的实时跟踪
- 进行深度市场分析 – 基于大量数据发现商业机会和趋势
- 优化运营决策 – 通过数据驱动的方式提高业务效率
随着电商行业的不断发展,电商数据采集API集成将变得越来越重要。Pangolin作为专业的数据服务提供商,不断优化其API功能和稳定性,为用户提供更好的数据采集体验。
在实际应用中,建议你根据具体需求选择合适的数据采集策略,合理控制请求频率,并建立完善的数据管理机制。同时,也要关注相关法律法规,确保数据采集活动的合规性。
希望这篇Pangolin Scrape API开发指南能够帮助你在数据驱动的商业竞争中获得优势。如果你在使用过程中遇到问题,建议查阅官方文档或联系技术支持获得帮助。
记住,掌握专业的Amazon数据抓取API教程不仅能提高工作效率,更能为你的业务决策提供强有力的数据支撑。开始你的数据采集之旅吧!